Geometry Chapter 9 Test Answers
-
one.
The point (five,-9) is the image under the translation (x,y) → (10 + 3,y + 2). What is the preimage?
-
A.
(two, -11)
-
B.
(8, -7)
-
C.
(2, -vii)
-
D.
(viii, -11)
-
-
2.
What rule describes the translation 4 units up and 12 units left?
-
A.
(ten,y) → (x + 4, y + 12)
-
B.
(10,y) → (x – 12, y - iv)
-
C.
(x,y) → (x + iv, y - 12)
-
D.
(x,y) → (10 - 12, y + four)
-
-
three.
ΔXYZ has vertices X(-5,2), Y(0,-four), and Z(3,three). What are the vertices of the paradigm of ΔXYZ under the translation (10,y) → (ten + 7, y - 5)?
-
A.
10'(2,-3), Y'(7,-9), Z'(10,-two)
-
B.
X'(-12,7), Y'(-seven,i), Z'(-iv,8)
-
C.
X'(-12,-three), Y'(-7,-9), Z'(-4,-two)
-
D.
X'(2,-three), Y'(x,-2), Z'(vii,-9)
-
-
iv.
What is the reflection paradigm of (five,-3) across the y-axis?
-
A.
(5, 3)
-
B.
(-five, three)
-
C.
(-five, -3)
-
D.
(three, 5)
-
-
5.
What is the reflection epitome of (v, -3) across the line y = -x?
-
A.
(-3, 5)
-
B.
(-three, -5)
-
C.
(3, -5)
-
D.
(three, 5)
-
-
half dozen.
What is the reflection epitome of (a,b) beyond the line y = -6?
-
A.
(a – 6,b)
-
B.
(a,b - 6)
-
C.
(-12 – a, b)
-
D.
(a, -12 – b)
-
-
7.
The preimage of a reflection lies in Quadrant II and the image is in Quadrant III. Which line could be the line of reflection?
-
A.
Y = 10
-
B.
Y = -10
-
C.
X-centrality
-
D.
Y-centrality
-
-
viii.
Name the image of X for a 240º counterclockwise rotation about the center of the regular hexagon.
-
A.
A
-
B.
Yard
-
C.
O
-
D.
H
-
-
9.
What is the image of (ane,-6) for a 90º counterclockwise rotation most the origin?
-
A.
(half dozen, 1)
-
B.
(-1, 6)
-
C.
(-6, -i)
-
D.
(-one, -half-dozen)
-
-
ten.
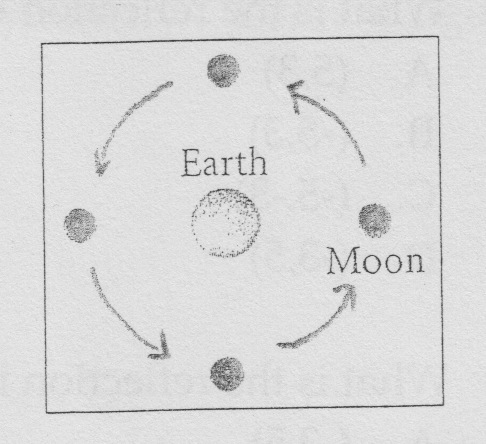
The same hemisphere of the moon always faces Earth. Thus, the motion of the moon about Earth for a given time interval can be modeled by a rotation. The heart of the rotation is the middle of the Earth. The angle of rotation is adamant by the time interval, given that one journey of the moon around Earth takes near 27 1/3 days.What rotation is modeled by the motion of the moon?
-
A.
A circle rotating about its center
-
B.
A circle rotation near a bespeak
-
C.
2 circles rotating effectually each other
-
D.
A circle rotating around a circumvolve
-
-
11.
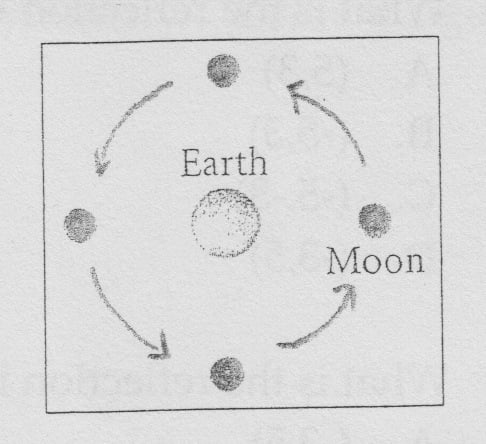
The aforementioned hemisphere of the moon always faces Globe. Thus, the move of the moon about Earth for a given time interval can be modeled by a rotation. The center of the rotation is the center of the Earth. The angle of rotation is determined past the time interval, given that one journey of the moon around Earth takes well-nigh 27 1/3 days.In how many days does the moon complete a 90º angle of rotation?
-
A.
Nigh four
-
B.
About 7
-
C.
Almost 14
-
D.
About 27
-
-
12.

Which figure does Not have rotational symmetry?
-
A.
A
-
B.
B
-
C.
C
-
D.
D
-
-
13.
Which figure, in general, has exactly two lines of symmetry?
-
A.
Pentagon
-
B.
Circle
-
C.
Square
-
D.
Rectangle
-
-
14.
Which quadrilateral has rotational symmetry but non reflectional symmetry?
-
A.
Nonisosceles trapezoid
-
B.
Kite
-
C.
Rhombus
-
D.
Parallelogram
-
-
15.
What is the smallest angle through which y'all can rotate a regular hexagon onto itself?
-
A.
30º
-
B.
60º
-
C.
90º
-
D.
120º
-
-
sixteen.
Find the image of P(11,-5) for the translation (ten,y) → (ten – 12, y – 6) followed by a reflection in ten = 0.
-
A.
(1, -11)
-
B.
(-1, eleven)
-
C.
(1, 11)
-
D.
(-1, eleven)
-
-
17.
A reflection in the y-centrality followed by a reflection in the 10-axis does Not give the same result every bit which of the following transformations?
-
A.
A reflection in the x-axis by a reflection in the y-axis
-
B.
A rotation of 180º
-
C.
A rotation of 90º followed by a reflection in the x-axis
-
D.
A reflection in the line y = x followed past a reflection in the line y = -ten
-
-
18.
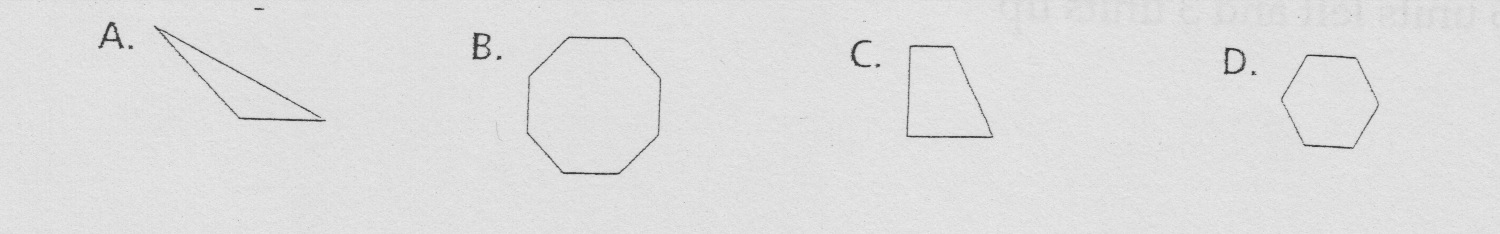
Which figure will Non tessellate a plane?
-
A.
A
-
B.
B
-
C.
C
-
D.
D
-
-
19.
Yous can tessellate a plane using a regular octagon together with which other type of regular polygon?
-
A.
Triangle
-
B.
Square
-
C.
Pentagon
-
D.
Hexagon
-
-
20.
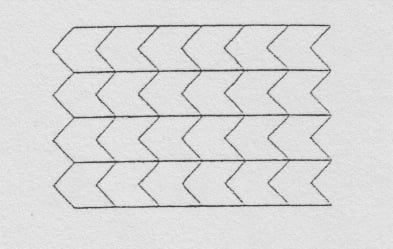
Which is Non a symmetry for the tessellation?
-
A.
Line Symmetry
-
B.
Translational symmetry
-
C.
Rotational symmetry
-
D.
Glide reflectional symmetry
-
Geometry Chapter 9 Test Answers,
Source: https://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/story.php?title=geometry-chapter-9-test-part-i
Posted by: gloverdebut1991.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Geometry Chapter 9 Test Answers"
Post a Comment